Windows Media Video (WMV) is a series of video codecs and their corresponding video coding formats developed by Microsoft. It is part of the Windows Media framework. WMV consists of three distinct codecs: The original video compression technology known as WMV, was originally designed for Internet streaming applications, as a competitor to RealVideo. The other compression technologies, WMV Screen and WMV Image, cater for specialized content. After standardization by the Society of Motion Picture and Television Engineers (SMPTE),[1][2] WMV version 9 was adapted for physical-delivery formats such as HD DVD and Blu-ray Disc and became known as VC-1.[3][4] Microsoft also developed a digital container format called Advanced Systems Format to store video encoded by Windows Media Video.
History[edit]
In 2003, Microsoft drafted a video compression specification based on its WMV 9 format and submitted it to SMPTE for standardization. The standard was officially approved in March 2006 as SMPTE 421M, better known as VC-1, thus making the WMV 9 format an open standard. VC-1 became one of the three video formats for the Blu-ray video disc, along with H.262/MPEG-2 Part 2 and H.264/MPEG-4 AVC.[3][4]
Container format[edit]
A WMV file uses the Advanced Systems Format (ASF) container format to encapsulate the encoded multimedia content. While the ASF can encapsulate multimedia in other encodings than those the WMV file standard specifies, those ASF files should use the .asf file extension and not the .wmv file extension.[5][failed verification]
The ASF container can optionally support digital rights management using a combination of elliptic curve cryptography key exchange, DES block cipher, a custom block cipher, RC4 stream cipher and the SHA-1 hashing function.
Although WMV is generally packed into the ASF container format, it can also be put into the Matroska[6] container format (with file extension .mkv), or AVI container format (extension .avi). One common way to store WMV in an AVI file is to use the WMV 9 Video Compression Manager (VCM) codec implementation.[7][8]
Video compression formats[edit]
Windows Media Video[edit]
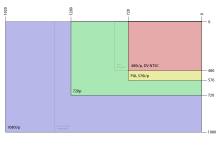
Diagram illustrating the relative frame sizes of several common video resolutions targeted by Windows Media Video 9 Professional, starting with 480p.
Windows Media Video (WMV) is the most recognized video compression format within the WMV family. Usage of the term WMV often refers to the Microsoft Windows Media Video format only. Its main competitors are MPEG-4 AVC, AVS, RealVideo, and MPEG-4 ASP. The first version of the format, WMV 7, was introduced in 1999, and was built upon Microsoft’s implementation of MPEG-4 Part 2.[9] Continued proprietary development led to newer versions of the format, but the bit stream syntax was not frozen until WMV 9.[10] While all versions of WMV support variable bit rate, average bit rate, and constant bit rate, WMV 9 introduced several important features including native support for interlaced video, non-square pixels, and frame interpolation.[11] WMV 9 also introduced a new profile titled Windows Media Video 9 Professional,[12] which is activated automatically whenever the video resolution exceeds 300,000 pixels (e.g., 528 px × 576 px, 640 px × 480 px or 768 px × 432 px and beyond) and the bitrate 1000 kbit/s[citation needed]. It is targeted towards high-definition video content, at resolutions such as 720p and 1080p.
The Simple and Main profile levels in WMV 9 are compliant with the same profile levels in the VC-1 specification.[13] The Advanced Profile in VC-1 is implemented in a new WMV format called Windows Media Video 9 Advanced Profile. It improves compression efficiency for interlaced content and is made transport-independent, making it able to be encapsulated in an MPEG transport stream or RTP packet format. The format is not compatible with previous WMV 9 formats, however.[14]
WMV is a mandatory video format for PlaysForSure-certified online stores and devices, as well as Portable Media Center devices. The Microsoft Zune, Xbox 360, Windows Mobile-powered devices with Windows Media Player, as well as many uncertified devices, support the format.[15] WMV HD mandates the use of WMV 9 for its certification program, at quality levels specified by Microsoft.[16] WMV used to be the only supported video format for the Microsoft Silverlight platform, but the H.264 format is now also supported starting with version 3.[17]
Windows Media Video Screen[edit]
Windows Media Video Screen (WMV Screen) are video formats that specialise in screencast content. They can capture live screen content, or convert video from third-party screen-capture programs into WMV 9 Screen files. They work best when the source material is mainly static and contains a small color palette.[18]
One of the uses for the format is computer step-by-step demonstration videos. The first version of the format was WMV 7 Screen. The second version, WMV 9 Screen, supports VBR encoding in addition to CBR.[18] Additionally there is MSA1 (aka “MS ATC Screen codec” or “MSS3”) which is used in Live Meeting 2007. FourCCs for the formats are MSS1, MSS2 and MSA1.[19]
Windows Media Video Image[edit]
Windows Media Video Image (WMV Image) is a video slideshow format. The format works by applying timing, panning and transition effects to a series of images during playback.[20] The codec achieves a higher compression ratio and image quality than WMV 9 for still images as files encoded with WMV Image store static images rather than full-motion video.
Since the format relies on the decoder (player) to generate video frames in real-time, playing WMV Image files even at moderate resolutions (e.g. 30 frames per second at 1024 px × 768 px resolution) requires heavy computer processing. The latest version of the format, WMV 9.1 Image, used by Photo Story 3, features additional transformation effects, but is not compatible with the original WMV 9 Image format.[20]
Hardware support for WMV Image is available from Portable Media Centers, Windows Mobile-powered devices with Windows Media Player 10 Mobile.[15]
Since no known domestic DVD player supports this format, users of Photo Story 3 wishing to generate material capable of being played in a DVD player will first have to convert to MPEG-2 before burning a DVD (average file sizes in MPEG-2 are 5 to 6 times the .wmv file).
Versions[edit]
| Public Name |
FourCC |
Description |
| Microsoft MPEG-4 version 1 |
MPG4 |
Video for Windows-based codec. Non-standard MPEG-4 codec incompatible with the later standardized version of MPEG-4 Part 2. |
| Microsoft MPEG-4 version 2 |
MP42 |
VfW-based codec. Non-compliant with finalized MPEG-4 part 2 standard. |
| Microsoft MPEG-4 version 3 |
MP43 |
VfW-based codec. Non-compliant with finalized MPEG-4 part 2 standard. Eventually locked for encoding only with ASF files (build 3688 and earlier could also encode to AVI).[21] |
| Microsoft ISO MPEG-4 version 1 |
MP4S |
DirectX Media Objects (DMO)-based codec. MPEG-4 Simple Profile compliant. |
| Microsoft ISO MPEG-4 version 1.1 |
M4S2 |
MPEG-4 Advanced Simple Profile compliant.[22] |
| Windows Media Video 7 |
WMV1 |
DMO-based codec. |
| Windows Media Screen 7 |
MSS1 |
DMO-based codec. Optimized for low-bitrate sequential screen captures or screencasts. Deprecated in favor of Windows Media 9 Screen codec. |
| Windows Media Video 8 |
WMV2 |
DMO-based codec. |
| Windows Media Video 9 |
WMV3 |
DMO-based codec. Video for Windows (VfW/VCM) version also available. [1] |
| Windows Media Video 9 Screen |
MSS2 |
DMO-based codec. Optimized for low-bitrate sequential screen captures or screencasts. |
| Windows Media Video 9.1 Image |
WMVP |
DMO-based codec. Optimized for encoding video from sequential bitmap images. Used, for instance, by Photo Story. |
| Windows Media Video 9.1 Image V2 |
WVP2 |
DMO-based codec. Optimized for encoding video from sequential bitmap images. Used, for instance, by Photo Story. |
| Windows Media Video 9 Advanced Profile |
WMVA |
DMO-based codec. Deprecated as non-VC-1-compliant. |
| Windows Media Video 9 Advanced Profile |
WVC1 |
DMO-based codec. VC-1 compliant format. |
Audio compression formats[edit]
The audio format used in conjunction with Windows Media Video is typically some version of Windows Media Audio, or in rarer cases, the deprecated Sipro ACELP.net audio format. Microsoft recommends that ASF files containing non-Windows Media formats use the generic .ASF file extension.
Players[edit]
Software that can play WMV files includes Windows Media Player, RealPlayer, MPlayer, Media Player Classic, VLC Media Player and K-Multimedia Player. The Microsoft Zune media management software supports the WMV format, but uses a Zune-specific variation of Windows Media DRM which is used by PlaysForSure. Many third-party players exist for various platforms such as Linux that use the FFmpeg implementation of the WMV format.
On the Macintosh platform, Microsoft released a PowerPC version of Windows Media Player for Mac OS X in 2003,[23] but further development of the software has ceased. Microsoft currently endorses the 3rd party Flip4Mac WMV, a QuickTime Component which allows Macintosh users to play WMV files in any player that uses the QuickTime framework, free of charge to view files but chargeable to convert formats.[24] The WMV installer is bundled with Microsoft Silverlight by default, installation without Silverlight can be accomplished with a “Custom” install. According to the Flip4Mac website, WMV files with DRM encryption are not compatible with the component.
Encoders[edit]
Many programs can export video in WMV format; a few examples are Windows Movie Maker, Windows Media Encoder, Microsoft Expression Encoder, Sorenson Squeeze,[25] Sony Vegas Pro,[26] AVS Video Editor, VSDC Free Video Editor, Telestream Episode, and Telestream FlipFactory.[27][28]
Programs that encode using the WMV Image format include Windows Media Encoder, AVS Video Editor, and Photo Story.
Digital rights management[edit]
While none of the WMV formats themselves contain any digital rights management facilities, the ASF container format, in which a WMV stream may be encapsulated, can. Windows Media DRM, which can be used in conjunction with WMV, supports time-limited subscription video services such as those offered by CinemaNow.[29] Windows Media DRM, a component of PlaysForSure and Windows Media Connect, is supported on many modern portable video devices and streaming media clients such as the Xbox 360.
Criticism[edit]
WMV has been the subject of numerous complaints from users and the press. Users dislike the digital rights management system which is sometimes attached to WMV files.[30] The loss of the ability to restore licenses for WMV files in the Windows Media Player 11 was not positively received.[30] The Microsoft Zune does not support the standard Windows Media DRM system, so that protected WMV files cannot be played.[31]
See also[edit]
- JPEG XR / HDHD, an image file format and format developed by Microsoft





Recent Comments